Describe the Main Uses of Atp in Cells
It is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell and can be compared to storing money in a bank. Why or why not.
Adenosine Triphosphate Atp Function In Cells
Muscle cells use ATP to produce movement.

. Kinases which are enzymes that. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Animals store the energy obtained from the breakdown of food as ATP.
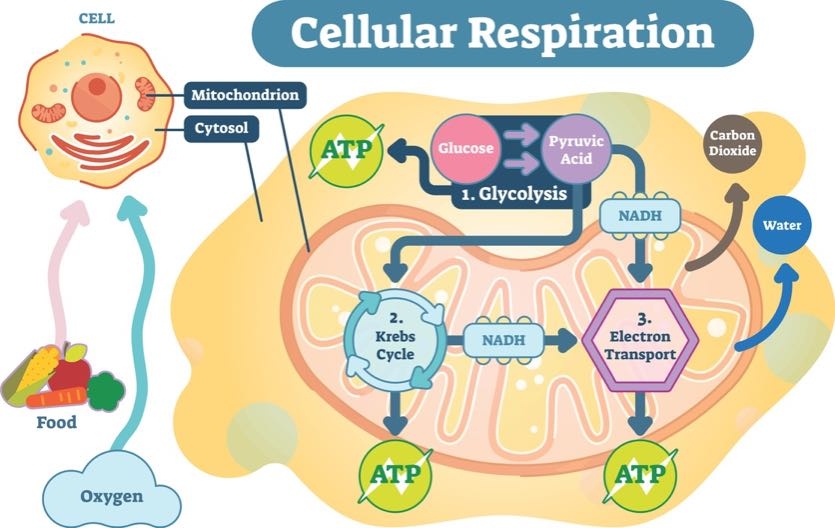
This is formed by the break down of carbohydrates lipid and fat. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. In this post I will try to explain very simply how ATP is produced in cells.
For energy to transport things from place to place within a cell. Adenosine Triphosphate ATP is the primary energy carrier in all living organisms on earth. Some ATP is made directly.
Explain why it is advantageous for cells to use ATP as an energy source rather than using glucose lipids or protein directly. Cancer cells use lactic acid fermentation producing lactic acid. ATP is a nucleotide that consists of three main structures.
And a chain of three phosphate. The nucleobase adenine is part of. The high energy bond is broken and a phosphoryl group is removed.
Cells generate ATP by adding a phosphate group Pi to ADP. ATP provides the energy for the contraction of spindle fibres separating chromosomes during Anaphase of mitosis and meiosis. Pyruvate is oxidized to form glucose and oxygen.
In addition to providing energy the breakdown of ATP through hydrolysis serves a broad range of cell functions including signaling and DNARNA synthesis. When the cell requires energy ATP is broken down through hydrolysis. Other functions of ATP include supplying the energy required for the muscle contraction circulation of blood locomotion and various body movements.
Recall DNA structure which consists of. ATP is the most important and mostly used compound in the cell for energy transfer reactions hence it is called energy currency of cell. ATP serves for making muscles contract including the heartbeat cilia beat and sperm swim.
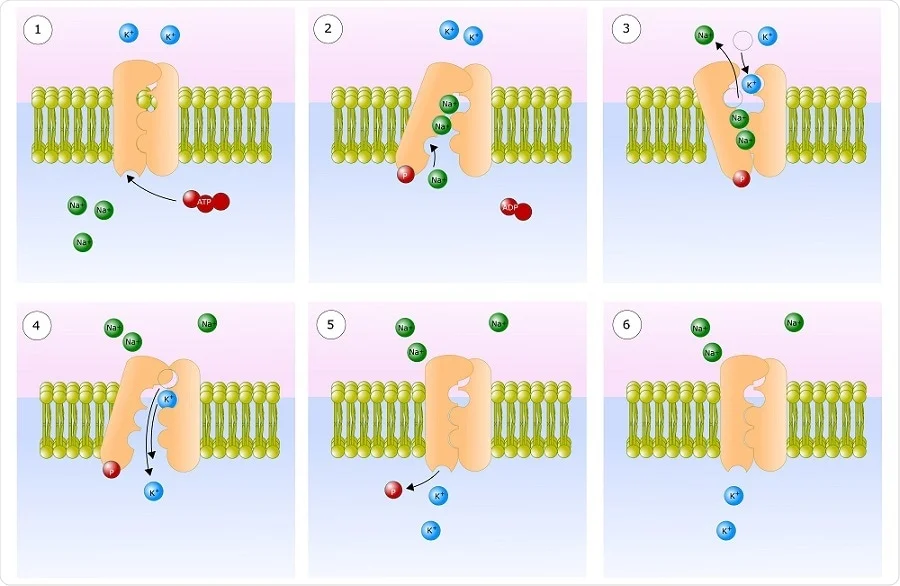
ATP is an energy storing molecule called adenosine triphosphate or ATP for short the cells energy currency. What is the role of ATP in the process of active transport. The nitrogenous base adenine.
The ATP is used for various cellular functions including transportation of different molecules across cell membranes. For pumping ions through cell membranes which is a basis for nerve action generating body heat and many other functions. During the complete oxidation of glucose cells have two ways of doing this.
These include intracellular signaling DNA and RNA synthesis Purinergic signaling synaptic signaling active transport and muscle contraction. Biochemical processes that utilise ATP include. ATP is the main carrier of energy that is used for all cellular activities.
ATPase is a hydrolysing enzyme so that a water molecule is needed but this is not normally shown in the equation. Textbooks often describe the mechanism of ATP production in cells in a very complicated way. A Describe how the hydrogen released during glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle results in the production of ATP.
ATP hydrolysis provides the energy needed for many essential processes in organisms and cells. ATP is a phosphorylated nucleotide. 3 Cells generate ATP by adding a phosphate group P i to ADP.
Cells need energy to make large molecules like hormones. ATP is commonly referred to as the energy currency of the cell as it provides readily releasable energy in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is the energy currency of life the way that individual cells store and use chemical energy.
Biosynthesis of macromolecules eg. OR active transport cell movement amino acid activation AVP. 100 1 rating ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosohate.
What are 3 things ATP is used for in cells. For powering mitosis and meiosis. It does this by shedding a phosphate group becoming adenosine diphosphate or ADP a highly energetic.
ATP can be used to store energy for future reactions or be withdrawn to pay for reactions when energy is required by the cell. 4 marks _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ b Using the information. ATP is the energy source for cells.
The energy transformation concept was established by Lipman 1941. Propagation of action potentials. ATP adenosine triphosphate ADP adenosine diphosphate P phosphate energy.
It synthesises 30 KJ per molecule. Polymer assembly Active transport eg. Microorganisms capture and store energy metabolized from food and light sources in the form of ATP.
Once a cell has made ATP it can use the ATP to fulfill any of its energy needs. ATP is the universal energy carrier in living org where hydrolysis of phosphate grps releases energy. The energy contained in ATP is used in synthesis carbohydrates proteins and lipids.
ATP is an instant source of energy within the cell. ATP provides the energy for the movement of vesicles either into or out of the cell. ATP is the energy currency of the cell.
ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is used to power a variety of cellular reactions. ATP is a signaling molecule used for cell communication. Endocytosis exocytosis Nerve transmission eg.
Many proteins bind together to form large complexes and multiple complexes form. Functions of ATP Energy Source. A The process of ATP hydrolysis.
Any food or other source of energy a cell takes in is converted to ATP in which form the mechanisms of the cell can easily use it. Substrate level phosphorylation oxidative phosphorylation Figs 21 and 22 are diagrams that show the main details of these two processes not drawn to the same scale. Hydrogen is also released and this can result in the production of more ATP.
B If a persons diet contained only sugar and protein no fat could this person still increase his or her percentage of body fat. When ATP is hydrolyzed and. Cancer cells rely on aerobic respiration producing carbon dioxide and ATP.
The flow diagram below shows some of the steps involved in glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle. Because the cancer cells cannot stop dividing what is the fate of pyruvate in these cells that exist in lowoxygen conditions. ATP help cells get energy for work and without ATP a cell will die.
I dont think its unreasonable. For synthesizing proteins nucleic acid and other molecules. As a cell makes a hormone molecule it breaks down molecules of ATP and uses the energy to make new bonds between smaller molecules in order to produce a larger one explain Drs.
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists

Adenosine Triphosphate Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica
0 Response to "Describe the Main Uses of Atp in Cells"
Post a Comment